Jan 23, 2023 | General Health
Arteries and Veins – How they play a role
Patients often come to the office complaining of cold feet as a result of varicose vein disease. Unfortunately, varicose vein disease not only doesn’t present with cold feet, but often can represent a more serious diagnosis.
The circulatory, or vascular system, consists of arteries and veins. Arteries are thick, muscular vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart throughout the body. Veins are low pressure, capacity vessels that return the oxygen-depleted blood back to the lungs.
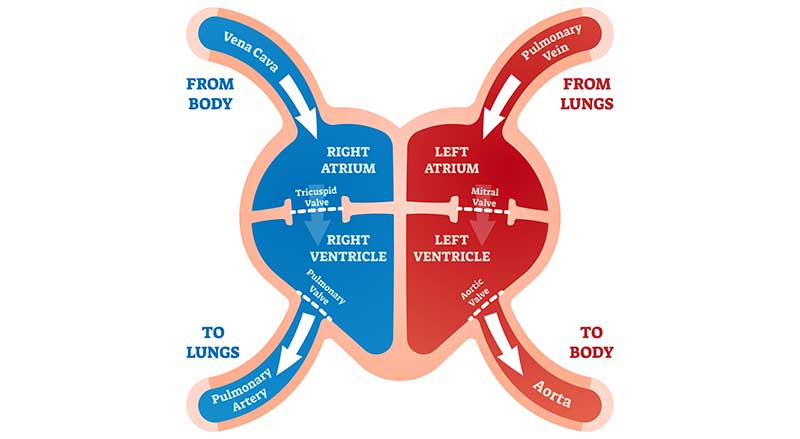
Blood is replenished with oxygen in the lungs. It is then sent to the heart to resend the oxygen-rich blood throughout the body by way of the arteries. This arterial to venous loop continues throughout a person’s life.
The question then remains as to why patients have cold feet if cold feet are not a symptom of varicose vein disease?
Nothing in the human body can be labeled as “simple”, but veins are simple when compared to their more sophisticated cousin, the artery.
Generally speaking, arteries deliver blood at a temperature of 98.6°F to the body. Blood cooler than this temperature is interpreted as cooler, or cold, by most people.
Basically, any factor that decreases the delivery of blood can result in cold feet. As the arteries deliver the blood to the feet, we must consider factors that slow the flow of blood to the feet.
Complicating this further, the feet are the “end of the line” for arterial circulation. That means the blood that flows to the feet and toes travels further from the heart than to any other part of the body.
Arteries are plagued by stenosis, or a narrowing of their diameter by atherosclerotic plaques. Stenosis occurs as a result of many insults with the primary culprits being hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and genetics.
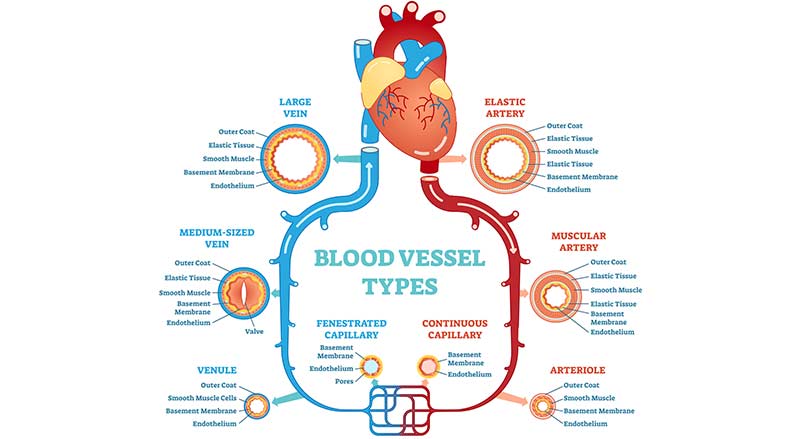
In addition, small arteries, called arterioles, regulate the pressure of the blood that reaches all parts of the body.
Arterioles are found between the arteries and capillaries. Factors that cause the arterioles to constrict will decrease blood flow, and subsequent warmth, to the feet and toes.
Many factors contribute to decreased circulation to the feet and toes. These include medications and caffeine intake from coffee, tea, and chocolate. Hypothyroidism and other diseases such as lupus and Raynaud’s may also be a factor.

Most patients believe that their cold feet are a symptom of varicose vein disease. In reality, the arteries and arterioles are the culprit.
While the symptoms may often be managed by wearing warm socks, exercising, and avoiding caffeine or tobacco, persistent symptoms should always be evaluated by a patient’s primary care doctor.
Mar 20, 2020 | Skin Conditions, Skincare
Prevent and treat dark spots on your skin with proper skincare and some helpful tips. Don’t be embarrassed by hyperpigmentation. Figure out the cause and treat the issue.
The reality is that hyperpigmentation occurs in more people than you may realize. Hyperpigmentation is a common problem that affects all skin types.
While this skin condition is often harmless, it could also be a sign of illness that requires medical treatment. It’s best to consult a doctor before taking action to remedy the issue.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a condition in which dark patches appear on the skin. This darkening of the skin occurs when melanocytes become hyper-stimulated.
In turn, from this excess stimulation, melanocytes create an increased production of melanin. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin it’s color. So, when our bodies begin to produce more of it, it causes us to tan or in this case, develop dark spots.
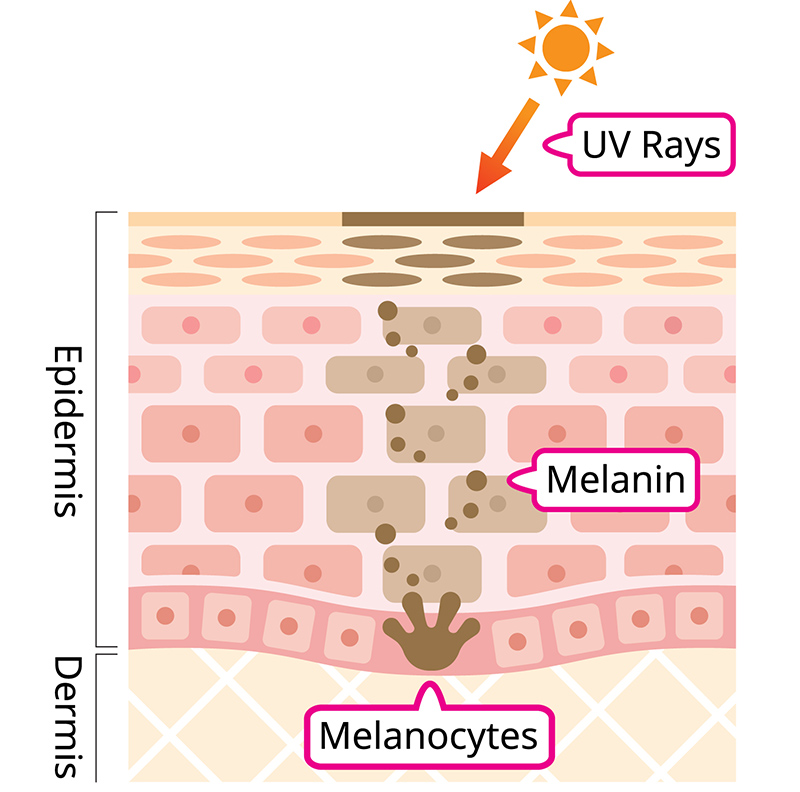
People with a fairer complexion have less melanin and tend to develop hyperpigmentation more easily than others. However, individuals with darker complexions may have more difficulty getting rid of hyperpigmentation.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
There are a variety of causes for hyperpigmentation. The causes range from simple day-to-day activities to possible warning signs of illness. Here’s what you should know:
Hyperpigmentation can occur as a result of excessive exposure to the sun. With sun damage, darker spots appear in areas that are always subjected to the sun i.e., face, arms, and legs.
Melasma is characterized by brown patches that commonly appear on women during pregnancy. Heredity, sun exposure, and hormones play key roles in its development.
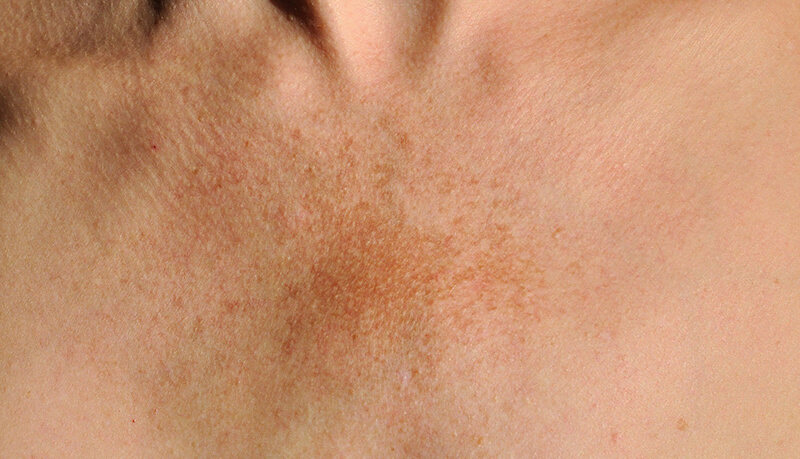
Inflammation can lead to discoloration of the skin. Dark spots can be triggered in areas that have become inflamed due to acne (acne scars), insect bites, or minor injuries.
Dark patches on the skin can also be a sign of serious illnesses such as lupus or cancer. Consult a doctor to rule these medical issues out.
Preventing Hyperpigmentation
The primary cause of hyperpigmentation is the sun. Avoid exposing yourself to its damaging rays for prolonged periods of time.
Sunburn leads to inflammation which is a big proponent of dark spots. Doctors recommend using a daily sunscreen with at least SPF 30 protection.
Since dark spots can also be caused by an injury, acne, or even a bug bite, avoid touching affected areas to prevent further inflammation.
Stay moisturized with ingredients that benefit the skin. Choose a product that will restore your skin’s barrier and boost cell turnover rate.
How to Treat Hyperpigmentation
If you have hyperpigmentation, the following will help reduce its appearance and minimize further damage:
- Vitamin C boosts collagen and helps reverse cell damage.
- Vitamin E protects skin from further damage and offers anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Hyaluronic acid offers additional moisture and speeds up wound healing.
- Retinol to boost cell turnover rate.
Consult a medical professional for further information about topical prescription treatments. These treatments may include products that offer hydroquinone, azelaic acid, or corticosteroids; agents that provide a bleaching effect.
For more serious skin issues, laser treatment, ablative or nonablative, can be effective.
Ablative lasers remove the top layer of skin, effectively erasing the skin issue.
Nonablative lasers, on the other hand, pass through the skin without removing any. Both laser types are used to correct hyperpigmentation, skin texture, and tone.








